What is Coronary Angioplasty?
The role of coronary arteries is essential in keeping the heart healthy. In some individuals, they become blocked or narrowed due to fatty deposits known as atheroma, that develop within the artery walls.
Coronary Angioplasty involves improving the supply of blood to the heart muscles by simply widening the narrowed or blocked coronary arteries. It ensures that the blood is flowing properly.
This treatment can also aid in relieving the angina symptoms. It also appears as an emergency treatment for individuals who are affected by a heart attack.
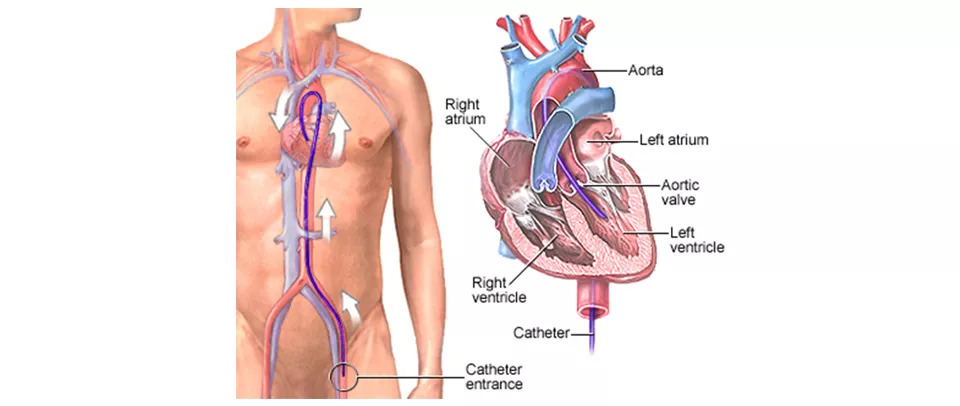
Types of Coronary Angioplasty
Balloon Angioplasty
It is the procedure used for widening narrowed or blocked coronary arteries. Here a catheter with a tiny balloon is guided to the blockage. Then the balloon is inflated for stretching open the blocked or narrowed artery, resulting in increased blood flow to the heart.
Carotid Angioplasty
The carotid angioplasty procedure is like the balloon angioplasty but is it accompanied by ‘stenting’. In this procedure, there is a thin tube used with the balloon at its end for opening artery, after which stenting is performed. Stenting involves placing a small metal coil inside the artery to prevent the artery from narrowing again.
Venous Angioplasty
This procedure is used for treating the vein blockages. The large veins, which are blocked or narrowed, can create severe pain and swelling. This treatment uses minimally invasive and image-guided procedures for diagnosing and rectifying the blockage.
Peripheral Angioplasty
It is the minimally invasive procedure. It is performed on blood vessels of the abdomen, leg and renal arteries. It is performed in the cardiovascular catheterization lab, under the local anaesthesia. An intravenous line, into your hand or arm will bring mediation for making this procedure comfortable. It widens the blocked region of the peripheral artery that supplies blood content to your heart.

